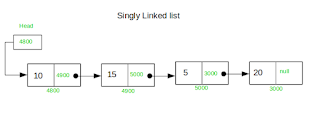
What is Linked List:
A linked list is a linear data structure, in which the elements are not stored at contiguous memory locations. The elements in a linked list are linked using pointers as shown in the below image:
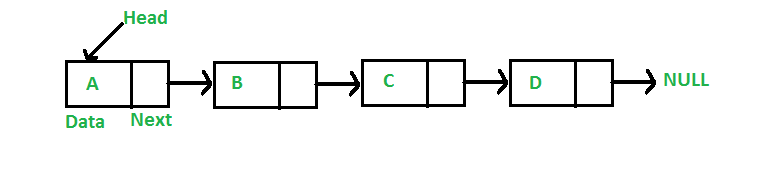

In simple words, a linked list consists of nodes where each node contains a data field and a reference(link) to the next node in the list.
Why Linked List?
Arrays can be used to store linear data of similar types, but arrays have the following limitations.
1) The size of the arrays is fixed: So we must know the upper limit on the number of elements in advance. Also, generally, the allocated memory is equal to the upper limit irrespective of the usage.
2) Inserting a new element in an array of elements is expensive because the room has to be created for the new elements and to create room existing elements have to be shifted.
Arrays can be used to store linear data of similar types, but arrays have the following limitations.
1) The size of the arrays is fixed: So we must know the upper limit on the number of elements in advance. Also, generally, the allocated memory is equal to the upper limit irrespective of the usage.
2) Inserting a new element in an array of elements is expensive because the room has to be created for the new elements and to create room existing elements have to be shifted.
Advantages vs Disadvantages of Linked List?
Advantages of Linked List
Dynamic Data Structure
Linked list is a dynamic data structure so it can grow and shrink at runtime by allocating and deallocating memeory. So there is no need to give initial size of linked list.
Insertion and Deletion
Insertion and deletion of nodes are really easier. Unlike array here we don’t have to shift elements after insertion or deletion of an element. In linked list we just have to update the address present in next pointer of a node.
No Memory Wastage
As size of linked list can increase or decrease at run time so there is no memory wastage. In case of array there is lot of memory wastage, like if we declare an array of size 10 and store only 6 elements in it then space of 4 elements are wasted. There is no such problem in linked list as memory is allocated only when required.
Implementation
Data structures such as stack and queues can be easily implemented using linked list.
Disadvantages of Linked List
Memory Usage
More memory is required to store elements in linked list as compared to array. Because in linked list each node contains a pointer and it requires extra memory for itself.
Traversal
Elements or nodes traversal is difficult in linked list. We can not randomly access any element as we do in array by index. For example if we want to access a node at position n then we have to traverse all the nodes before it. So, time required to access a node is large.
Reverse Traversing
In linked list reverse traversing is really difficult. In case of doubly linked list its easier but extra memory is required for back pointer hence wastage of memory.
There are types of Linked List, which is :
- Singly Linked List
It is the most common. Each node has data and a pointer the next code
- Doubly Linked List
Add a pointer to the previous node in a doubly-linked list. Thus, we can go in either direction, forward and backward
- Circular Singly Linked List
The last node contains a pointer to the first node. We can have a circular singly linked list as well as a circular doubly linked list. There is no storing of NULL values in the list
- Circular Doubly Linked List
It is similar to a circular single linked list, but the total pointer in each node here is two pointers. The more complex type of data structure in which a node contains pointers to its previous node as well to the next node. The circular doubly linked list doesn't contain NULL in any of the nodes. The last node of the list contains the address of the first node of the list. The first node of the list also contain address of the last node in its previous pointer.